System: process, thread, and files
Part 1: Processes and Threads
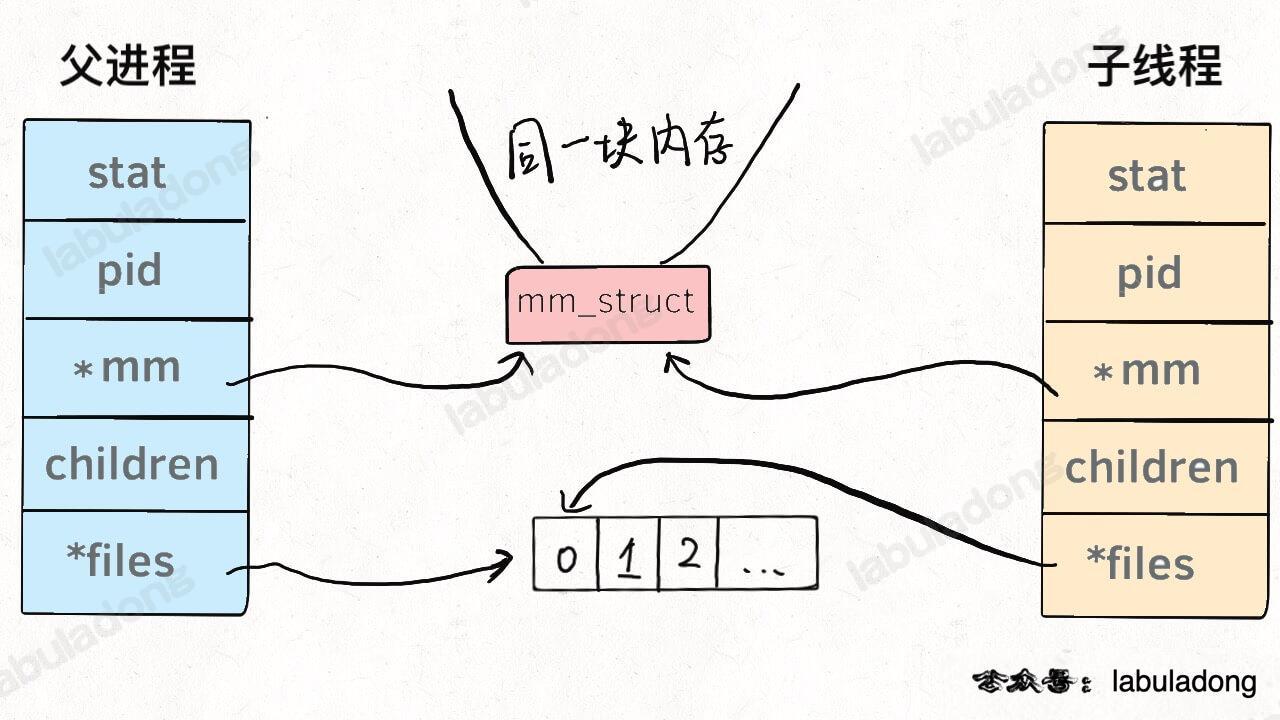
- Process and threads use the same
task_structstruct task_struct { long state; struct mm_struct *mm; pid_t pid; // 指向父进程的指针 struct task_struct __rcu *parent; // 子进程列表 struct list_head children; // 存放文件系统信息的指针 struct fs_struct *fs; // 一个数组,包含该进程打开的文件指针 struct files_struct *files; }; - Threads inherits parent process’s memory and files
- but child process copies parent’s memory and files
- so threads need lock, but processes don’t
- Both creation in Linux are fast
- process creation uses
copy-on-write, so only copies parent’s memory space when write
- process creation uses
Part 2 - Programming Concurrency
1 - Thread counter with mutex
int counter = 0;
mutex mtx;
void incr(int n){
mtx.lock();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
counter ++;
}
mtx.unlock();
}
int main(){
thread threads[5];
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
threads[i] = thread(incr, 1000);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
threads[i].join();
}
// put this after join threads
cout<<"counter is "<< counter<<endl;
}